Google has announced major updates to its search engine to better combat the growing problem of AI-generated explicit deepfakes. These updates are designed to enhance user protection by improving how the search engine filters out non-consensual explicit content and making it harder for such material to appear in search results. As the use of AI for creating realistic yet harmful content increases, Google is stepping up its efforts to address this issue.
What’s Happening & Why This Matters
Google is implementing a series of changes to its search algorithm and content removal processes to tackle the issue of explicit deepfakes more effectively. One of the key updates is the introduction of enhanced safety features that streamline the process for removing non-consensual explicit images from search results. When users successfully request the removal of an explicit deepfake, Google’s systems will now automatically work to filter out related explicit content in future searches. This proactive approach means users won’t have to repeatedly flag similar images, as the system will handle these cases automatically.
The search engine’s algorithm has also been refined to prioritize non-explicit, high-quality content in search results, particularly when users search for potentially harmful material. For example, if someone searches for deepfake images of a specific individual, Google will ensure that credible sources like news articles are shown first, rather than explicit content. Additionally, websites that are known for hosting non-consensual AI-generated explicit material will be penalized in search rankings, making it more difficult for them to appear prominently in search results.
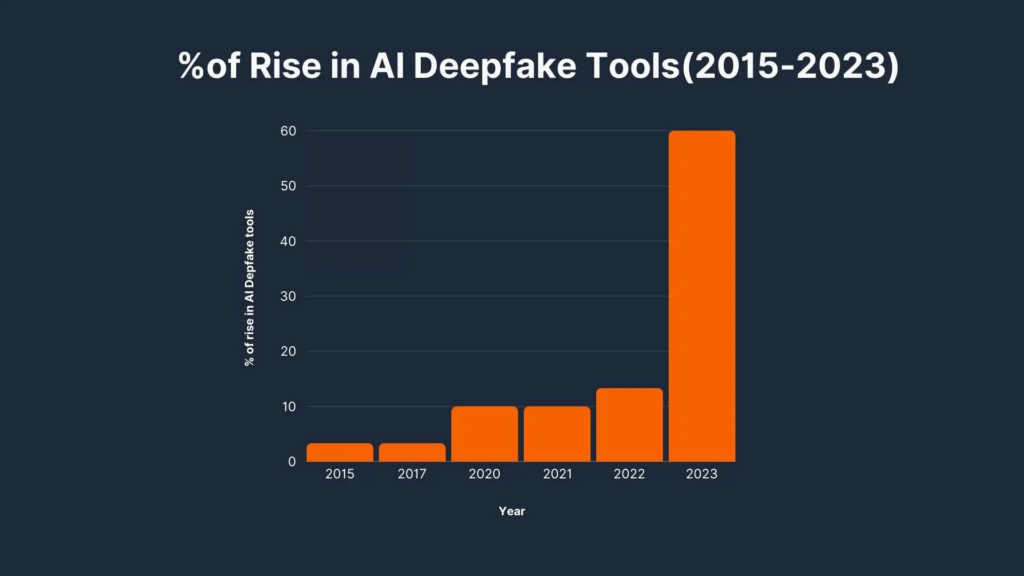
Google is also focusing on the challenging task of distinguishing between real explicit content and AI-generated fake images. This task is particularly difficult due to the sophistication of AI technologies, but Google is making strides in addressing the issue. The company reports that its recent updates have already led to a 70% reduction in user exposure to explicit deepfake content, demonstrating the effectiveness of these changes.
The issue of deepfakes goes beyond explicit content, with serious implications for misinformation and political manipulation. Earlier this year, deepfake videos of political figures like President Joe Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris circulated widely on social media, raising concerns about the potential for AI-generated content to influence public opinion and elections.
In response to these concerns, lawmakers in the U.S. are pushing for new legislation to protect individuals from the harmful effects of non-consensual deepfakes. The Senate recently passed the Defiance Act, which allows victims to sue those responsible for creating or sharing unwanted sexual deepfakes. In addition, Senator Ted Cruz has introduced the Take It Down Act, which seeks to make the publication of non-consensual sexual deepfakes a federal crime and impose stricter regulations on social media platforms.
These legislative efforts reflect the growing awareness of the dangers posed by deepfake technology and the need for stronger protections against its misuse. As AI tools become more powerful and accessible, the potential for harm increases, prompting both tech companies and governments to take action.
TF Summary: What’s Next
Google’s recent updates to its search engine represent a crucial step in addressing the challenges posed by AI-generated content, particularly explicit deepfakes. The improvements have already shown positive results, reducing the visibility of harmful material in search results. However, Google recognizes that more work is needed to fully address the issue and prevent the misuse of deepfake technology. As discussions around deepfake legislation continue and new laws are introduced, tech companies like Google will likely face additional pressure to strengthen their strategies for managing and mitigating the risks associated with AI-generated content. The ongoing development of AI and its potential for misuse will require continuous adaptation to protect users and maintain the integrity of online platforms.
— Text-to-Speech (TTS) provided by gspeech


