Technology Speeds Advancements in Care, Detection, and Prevention
The state of medicine saw advancements this year. Three stories convey an uplifting arc: VR holograms assist in operating rooms, AI sleuths out chronic stress inside adrenal glands, and a gene therapy reduces a rare disease from a child’s life. Each story represents medicine crossing into software, imaging, and computation. Each success exhibits clinical judgement melding with digital tools. And each story signals a new standard in medical care.
Holographic tools are changing surgical planning. Deep-learning models read stress markers with precision. Gene therapy uncover durable power inside urgent cases. When medicine leverages sensors, visual systems, and computing power, medical practitioners gain clarity. Patients gain time.
What’s Happening & Why This Matters
Holograms Enter Surgical Planning
Surgeons use VR systems from HoloCare to rehearse complex procedures. The platform builds 3D holograms from standard MRI and CT data. Doctors step inside a liver or organ model. They rotate the structure, slice, and mark tumour margins. They test different surgical routes.
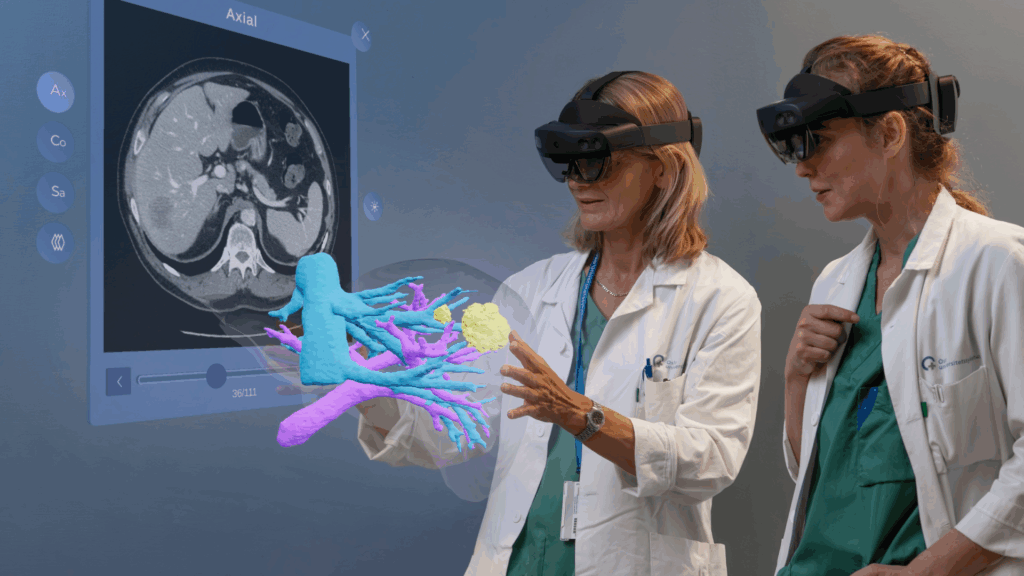
Teams also use the models to settle disagreements fast. Junior surgeons speak more. Senior surgeons see structural details in new ways. Computation reduces guesswork. The design lead at HoloCare describes the benefit plain: the system delivers spatial clarity and anatomical insight. Surgeons test resection plans. They calculate preserved liver volume, track tumour positions, and remove uncertainty from complex cases.
One surgeon even reversed an “inoperable” call after exploring the 3D model. The patient lived. The case shows a pattern where clinical images gain depth. From that depth, clinical decisions are increasingly precise.
AI Detects Chronic Stress Inside the Body
Another story connects medicine and computation from a different angle. A study from RSNA researchers shows that AI models can read chronic stress from routine chest CT scans. The model measures adrenal-gland volume. The adrenal glands control hormones tied to stress and metabolism. Oversized glands signal sustained stress exposure.
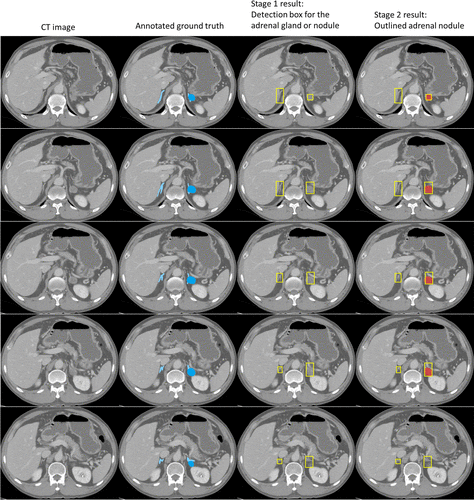
Researchers compared gland measurements against cortisol levels, BMI, blood pressure, and patient-reported stress. The results matched across metrics. The model flagged long-term stress responses in thousands of scans. One researcher stated the impact: AI reveals the “long-term burden of stress inside the body” with tools hospitals already use.
The model proposes a door into silent risk categories: heart failure, depression, metabolic strain. It even creates a consistent measure across large patient groups — something questionnaires and cortisol spikes never delivered cleanly. The study notes that poor scans create poor outcomes, so clinicians confirm AI suggestions. But the core insight stands: AI-assisted medical imaging identifies stress as a biological structure, not a mood.
Unique Gene Therapy Saves Lives
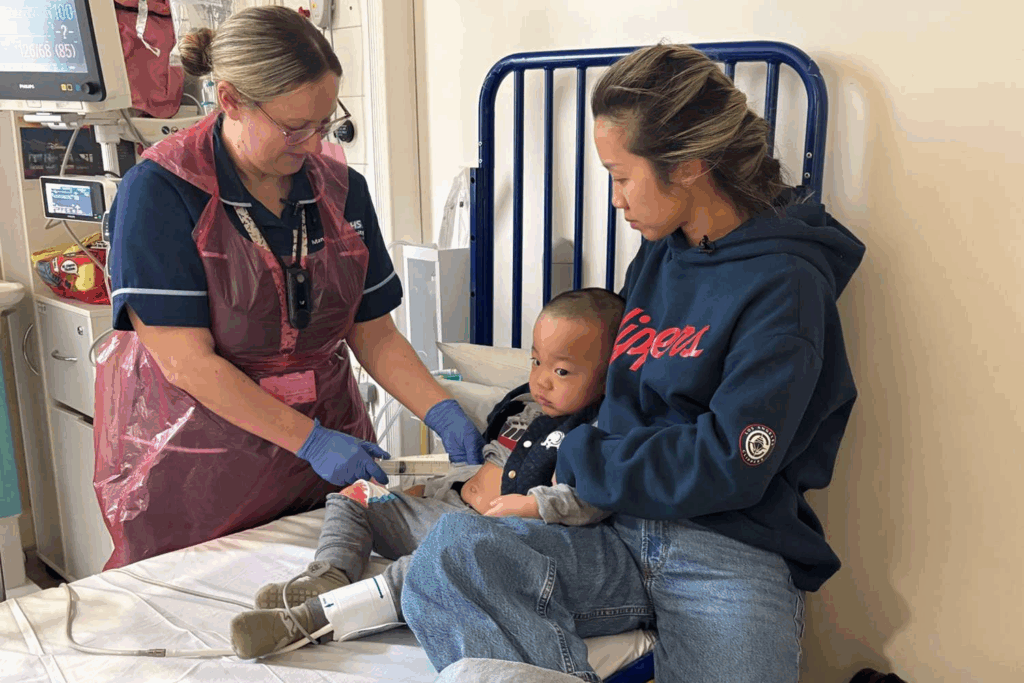

The third story adds raw human stakes. A boy, Oliver Chu, diagnosed with Hunter syndrome, a rare genetic disorder, received a custom gene therapy intervention. The therapy delivers a corrective enzyme to Chu’s system. The treatment removes symptoms and allows normal development. Chu’s case shows gene therapy is not limited to research labs. It can meet real families with real urgency.
The therapy also signals a shift in genetic medicine: bespoke treatments are an avenue to curb rare diseases with small patient populations. Doctors do no have to rely on drugs solely. They can work with precision tools tuned to DNA errors inside single cases. In worldwide medicine, regulators should support gene-therapy pipelines. Pharmaceutical groups should invest more. Hospitals should establish refined delivery protocols. Collectively, families gain options never available before.
TF Summary: What’s Next
Three threads merge into one idea: imaging, computation, and biology now operate as one system. VR gives surgeons deeper vision. AI gives clinicians objective metrics for stress. Gene therapy gives patients cures tailored to genetic faults. Medical care changes shape. Doctors gain digital partners. Patients gain longer horizons.
MY FORECAST: Hospitals adopt VR across organ systems. Chronic stress becomes a measurable biomarker in every major health network. Gene therapy expands into more rare-disease categories. Medicine enters a high-tech era with tighter loops, richer images, stronger data, and clearer interventions.
— Text-to-Speech (TTS) provided by gspeech