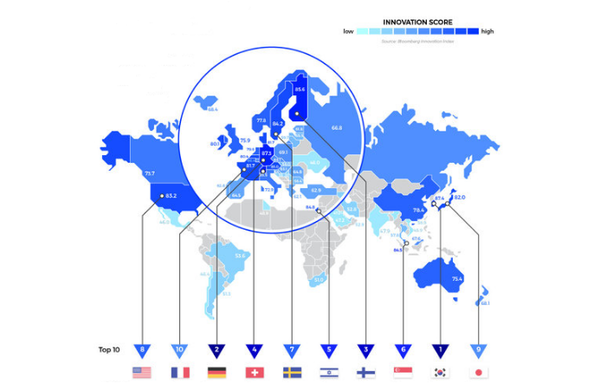
China officially entered the top 10 most innovative countries in the world, surpassing Germany for the first time in the United Nations’ Global Innovation Index (GII). China’s advancement is a coup and milestone for the world’s second-largest economy. China’s focus on research and development (R&D) continues at an unprecedented pace.
What’s Happening & Why This Matters
The Global Innovation Index, which evaluates 139 economies using 78 indicators, shows a reshuffling of the global innovation hierarchy. Switzerland remains in first place — a position it has held since 2011 — followed by Sweden and the United States. China now sits at 10th place, replacing Germany, which fell to 11th place.
China’s rise comes as the country rapidly increases private-sector financing for innovation and technology. According to the report, China is projected to become the world’s largest R&D spender. They are narrowing the gap with traditional leaders like the U.S., Japan, and Germany.
In 2024, China accounted for roughly 25% of all international patent applications, reinforcing its reputation as the largest global source of patents. By comparison, the U.S., Japan, and Germany combined made up 40% of applications. However, they experienced slight declines.
“The challenge for Germany is how, alongside its strong, decades-long status as a powerful engine of industrial innovation, to become a powerhouse of digital innovation,” said Daren Tang, director general of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), which publishes the index.
Global Trends and Challenges
The outlook for global innovation appears less promising. The GII report warns of declining global investment in R&D. It predicts that growth will slow to 2.3% this year, down from 2.9% in the previous year. This marks the slowest rate of R&D growth since the aftermath of the 2010 financial crisis.
Sacha Wunsch-Vincent, co-editor of the report, noted that Germany’s drop in ranking does not signal immediate concern. Instead, it reflects structural changes in how innovation is measured. It does not account for geopolitical factors, such as tariffs imposed by the Trump administration.
Other countries in the top 10, ranked between the U.S. and China, include South Korea, Singapore, the United Kingdom, Finland, the Netherlands, and Denmark. Each has built strong ecosystems for technology, digital infrastructure, and advanced manufacturing. These elements help them maintain their competitive edge.
Why It Matters for China and Germany
For China, this achievement validates its long-term strategy of investing heavily in science, technology, and innovation. By leading in international patents and approaching parity in R&D spending, China positions itself as a dominant force in the global technology economy.
Germany, meanwhile, faces a crossroads. Historically known for its industrial innovation in sectors including automotive and manufacturing, it must now accelerate its digital transformation. This is essential for competing in areas such as artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and advanced software engineering.
TF Summary: What’s Next
China’s rise into the top 10 most innovative nations signals a shift in the global balance of innovation power. With increased R&D spending and patent activity, China is poised to challenge the U.S. and Europe across key technology sectors.
MY FORECAST: The ranking drop is a wake-up call for Germany. This may be the impetus to shift from traditional industrial strengths toward digital-first strategies. The next decade’s investments can determine whether Germany can reclaim its top 10 spot. Falling behind in the innovation leadership race is not an option.
— Text-to-Speech (TTS) provided by gspeech