The European Union has initiated a series of investigations targeting Big Tech giants Apple, Google, and Facebook’s parent company, Meta, under the new Digital Markets Act (DMA). This landmark legislation aims to foster competition within digital services by ensuring that dominant online platforms provide users and competitors with more freedom and opportunities. With the threat of “heavy fines” looming, these probes mark a significant moment in the EU’s efforts to regulate the digital marketplace and could have profound implications for how Big Tech operates within Europe.

What’s Happening & Why This Matters
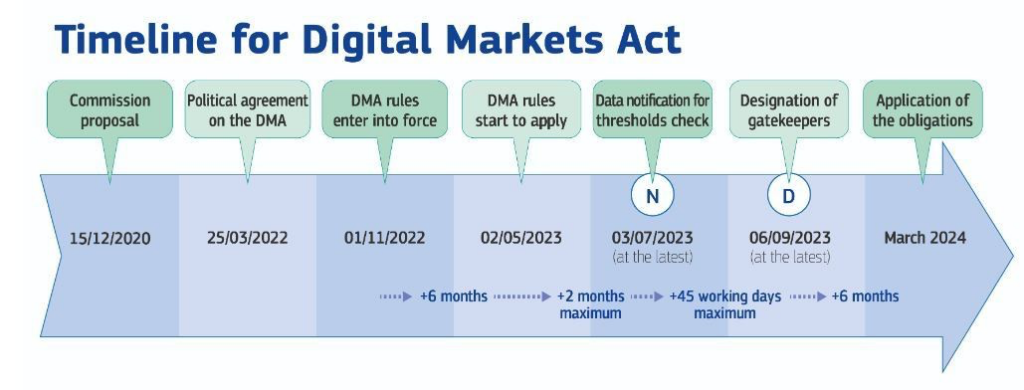
The DMA is Europe’s bold attempt to level the playing field in the digital sector. By requiring tech behemoths to open up their ecosystems, the act seeks to prevent the accumulation of power and data by a few dominant entities, thus promoting healthier competition and innovation. Key stipulations include allowing users more choice and developers more freedom to operate outside the major app stores without punitive charges.
The Allegations and Responses
- Meta’s “Pay or Consent” Model: The European Commission is scrutinizing Meta’s subscription service, which offers an ad-free experience for a fee, fearing it doesn’t offer a genuine choice to users unwilling to consent to data collection.
- Apple and Google’s App Stores: The focus here is on whether these platforms restrict developers’ abilities to communicate directly with users or to promote offers outside the app stores, potentially breaching the DMA’s provisions.
- Google Search: Concerns are raised about whether Google’s practices unfairly favor its services over third-party options in search results, compromising fairness and neutrality.
The Potential Impact
Should the investigations confirm violations of the DMA, the implicated companies could face fines up to 20% of their global revenue for repeated offenses, translating into billions of dollars. Beyond financial penalties, these probes could necessitate substantial changes to Big Tech’s business models and operational practices within the EU, particularly concerning data privacy, app store policies, and platform neutrality.
Responses from the companies highlight a commitment to compliance, with each outlining steps taken to align with the DMA’s requirements. Yet, there’s a clear tension between regulatory expectations and Big Tech’s operational norms, setting the stage for an extended dialogue on the balance between innovation, competition, and regulation.
TF Summary: What’s Next
As the EU presses forward with its investigations under the DMA, the outcomes could redefine the operational landscape for Big Tech in Europe and potentially beyond. With the global spotlight on these proceedings, the tech industry and regulatory bodies worldwide will closely watch how these disputes unfold, potentially influencing future digital policy and regulation. This pivotal moment underscores the ongoing debate around digital sovereignty, competition, and the role of Big Tech in shaping our digital futures.


