I’m looking for a new primary TV for viewing shows, sports, and PlayStation gaming. It’s been a while since I’ve done this, so what should I buy? What makes the most sense? Best viewing? Best price? In the ever-evolving space of television technology, it’s easy to get lost in the sea of abbreviations and technical jargon. Whether you’re setting up a new home theater or just looking to upgrade your current TV, understanding the different types of display technology is crucial. This article will break down the key differences between LED, OLED, QLED, QNED, and QD-OLED technologies to help you make an informed decision.
Choosing the right TV can be a daunting task with so many options on the market. Each type of display technology offers unique benefits and caters to different viewing preferences and environments. This guide seeks to clarify the various technologies and help you find the best fit for your needs.
EXPLAINED — LED Technologies
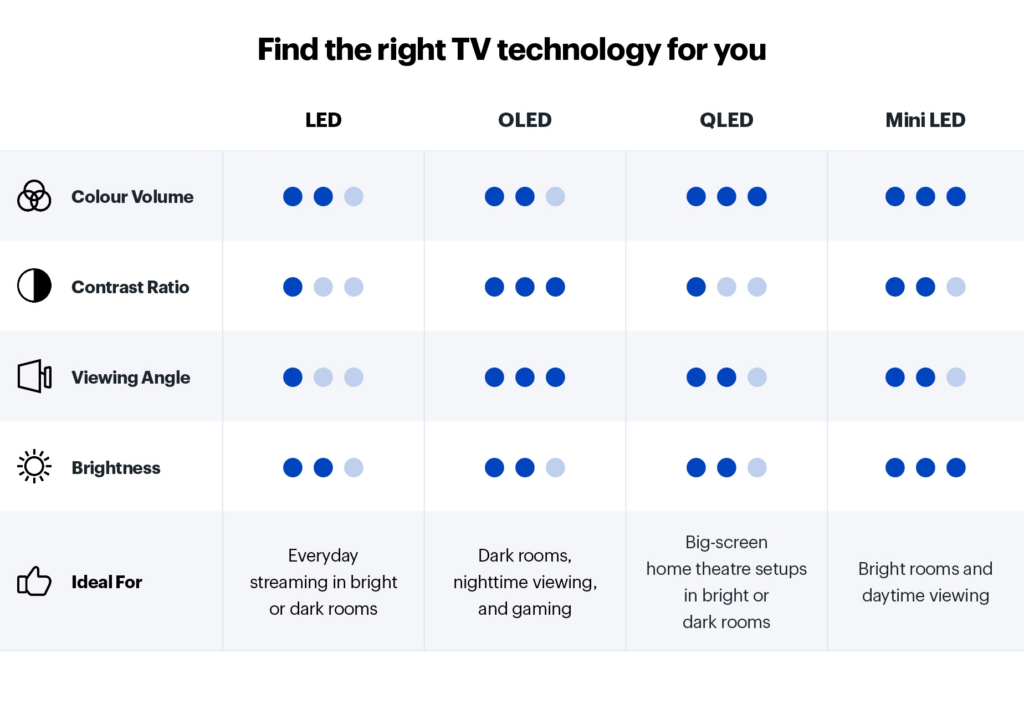
Light Emitting Diode (LED) TVs are perhaps the most common type of TV display technology. Technically, they are LCD screens backlit by LEDs. These TVs are popular for their affordability, brightness, and availability in various sizes. They are a great choice for general use, especially in well-lit environments.
- Brightness: LED TVs are among the brightest, making them suitable for rooms with lots of natural light.
- Price Range: Available from budget-friendly models to high-end sets with additional features.
- Gaming: High refresh rates make them a good choice for gaming.
- Size and Weight: Generally heavier and thicker than other types but still wall-mountable.
OLED TVs
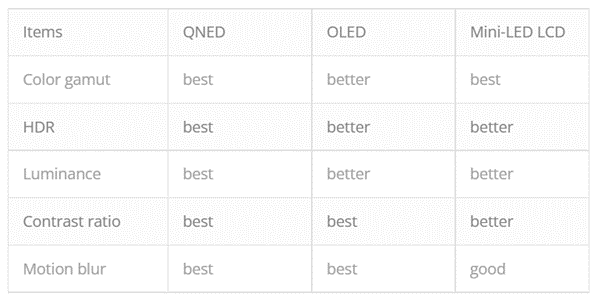
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) TVs do not have a backlight. Instead, each pixel emits its own light, allowing for perfect blacks and vibrant colors. This technology is ideal for dark rooms and home theaters.
- Image Quality: Exceptional with true blacks and vibrant colors.
- Brightness: Not as bright as LED TVs, which may be a drawback in brightly lit rooms.
- Design: Thinner and lighter due to the lack of a backlight.
- Price: Typically more expensive, but mid-priced models are becoming more available.
QLED, QNED, and QD-OLED TVs
Quantum Dot technologies like QLED, QNED, and QD-OLED enhance color and brightness by using quantum dots.
- QLED (Quantum Dot LED): Uses quantum dots to enhance color accuracy and brightness, suitable for bright environments.
- QNED (Quantum Dot NanoCell LED): Combines quantum dots and NanoCell technology with mini-LED backlighting, offering excellent color contrast and brightness.
- QD-OLED: A hybrid of OLED and quantum dot technology, providing the benefits of OLED with increased brightness and color range.
What is HDR?

HDR stands for High Dynamic Range (HDR). On top of tv resolution (i.e., 1080p, 4K, or 8K), HDR-capable televisions increase visual clarity and processing. HDR formats improve picture quality by enhancing contrast and color accuracy for still and moving imagery. The most common and popular formats are SDR, HDR10 and Dolby Vision.
- SDR:
- HDR10: The standard HDR format used in all 4K UHD TVs. Uses static metadata, which may not adjust optimally for all scenes.
- HDR10+:
- Dolby Vision: Uses dynamic metadata to adjust settings scene-by-scene, providing a more consistent and high-quality viewing experience.
TF Summary: What’s Next
TV technology continually advances so consumers can expect even more improvements in display quality and performance. Understanding the differences between LED, OLED, QLED, QNED, and QD-OLED technologies is helpful in making an informed decision that best suits your viewing habits and environment. Future developments will focus on enhancing brightness, color accuracy, and the overall viewing experience. This makes purchasing a new TV, yet daunting.


