Faults Caused Crashing in 13th-, 14th-gen CPUs
Intel has successfully tracked down and addressed a persistent issue causing crashes in its high-end 13th and 14th-generation desktop CPUs, including the Core i9-13900K and 14900K models. These crashes, particularly prevalent during gaming sessions, have been a source of frustration for many users. The company has now identified the root cause of the problem and plans to release a microcode update to resolve it.
What’s Happening & Why This Matters
Over the past several months, Intel has been investigating reports of crashes affecting its high-end 13th and 14th-generation desktop CPUs. Initially, the company responded by requiring third-party motherboard manufacturers to adhere strictly to Intel’s recommended default power settings. However, this measure did not fully resolve the issue, prompting further investigation.
Intel’s thorough investigation revealed that the crashes were caused by a microcode algorithm error. This error resulted in incorrect voltage requests being sent to the processor, causing it to receive too much power. Over time, this excess power degraded the stability of the processors, leading to the observed crashes and instability.
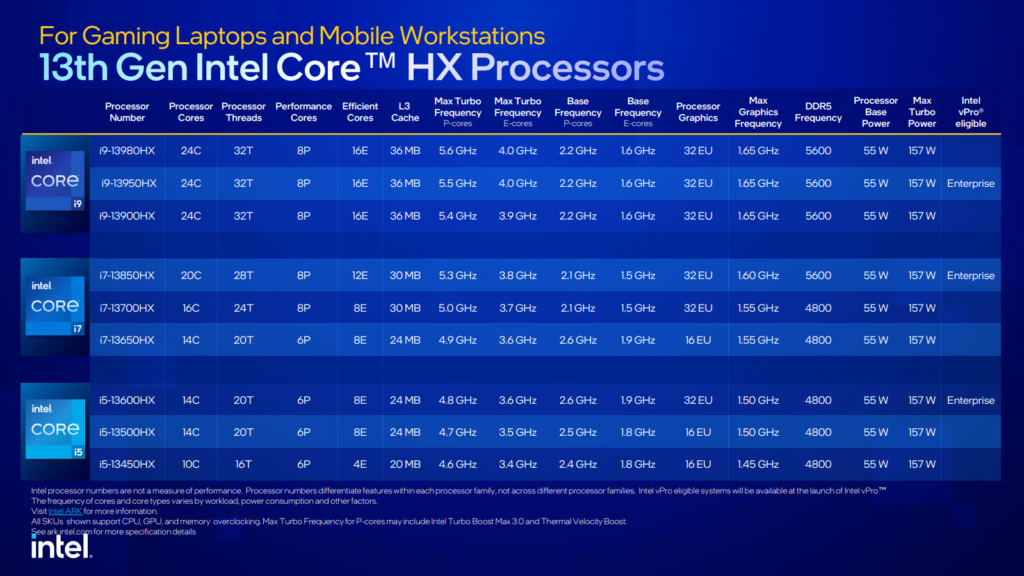
To address this issue, Intel has developed a microcode update designed to correct the voltage request algorithm. This update will be provided to motherboard manufacturers by mid-August, following full validation. Users will need to apply a BIOS update to their systems to implement this fix.
For users whose CPUs have not yet exhibited stability problems, the microcode update should prevent any future issues. However, for those already experiencing crashes and instability, the damage caused by the excess power is irreversible. Intel has stated that it will continue to replace defective CPUs to ensure customer satisfaction and system reliability.
The problem specifically affects the Raptor Lake architecture used in the 13th and 14th-generation processors. These processors feature higher clock speeds, more cache memory, and additional E-cores compared to the previous generation. The 12th-generation Alder Lake processors, which use a different architecture, have not shown similar issues.
In addition to the microcode-related problems, Intel confirmed that an unrelated manufacturing issue involving oxidation affected some early 13th-generation chips. This manufacturing issue was resolved in 2023 and is not connected to the crashes and instability that the microcode update aims to fix.
TF Summary: What’s Next
Intel’s proactive approach in identifying and addressing the CPU crashes demonstrates its commitment to maintaining high standards of performance and reliability. As the microcode update becomes available, users are encouraged to update their BIOS to prevent potential stability issues. Intel’s ongoing support for replacing defective processors ensures that affected users can maintain the integrity of their systems. The insights gained from resolving this problem are expected to enhance the stability and performance of future processor releases, ultimately benefiting the user experience.
— Text-to-Speech (TTS) provided by gspeech