Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the way we consume information, but AI-generated summaries are facing growing scrutiny. Meta is testing AI-powered chat summaries in WhatsApp and Instagram, aiming to help users catch up quickly. Meanwhile, Wikipedia paused its AI summary trial after editors raised concerns about the accuracy and credibility of the summaries. TF explores both developments and their impact on AI in content summarization.
What’s Happening & Why This Matters
Meta is rolling out a new feature called Summarize with Meta AI on WhatsApp for Android users. This button, located above unread messages, provides a quick summary of long conversations. Users must enable a privacy option called Private Processing, which ensures that message data stays confidential and inaccessible to Meta or WhatsApp during AI processing.
The feature doesn’t work if Advanced Chat Privacy is turned on, which prevents chat export. Meta is also experimenting with AI summaries for Instagram Direct Messages (DMs), though availability remains limited. Alongside this, Meta is testing AI-driven direct messaging capabilities for its newer app, Threads.
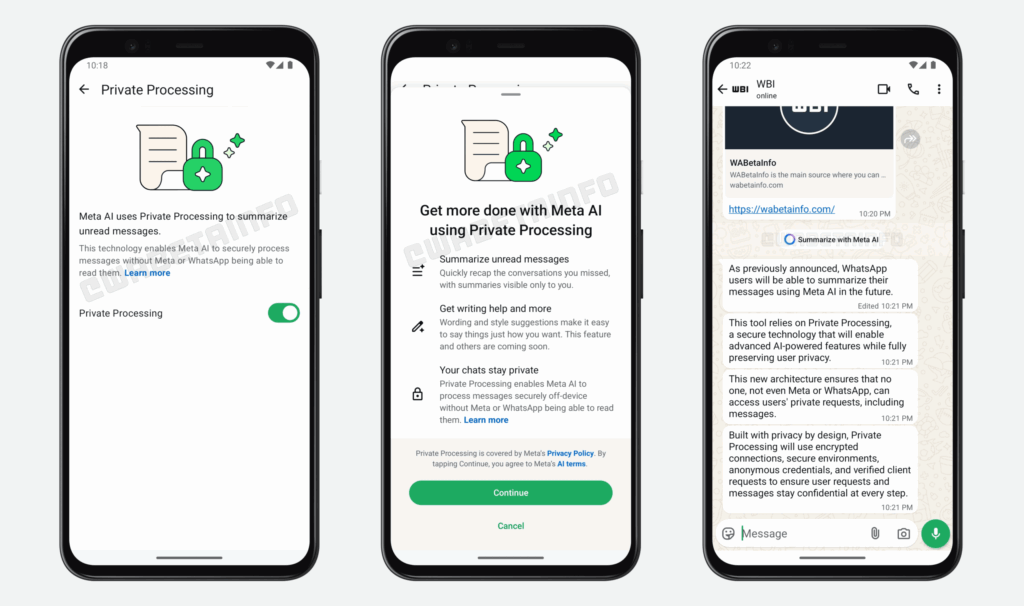
The features represent Meta’s efforts to integrate AI as a useful assistant in everyday communication. The company also has a writing assistant on Instagram called Rewrite, which uses Meta AI to improve captions and messages.
However, AI-generated summaries have a mixed track record. Earlier this year, Apple paused its AI news notification summaries after detecting false information. Accuracy concerns remain a challenge for AI in content summarization.

On the other side, Wikipedia began testing AI summaries on mobile devices in early June 2025. The trial showed a “simple summary” above the articles, flagged as “unverified.” The summaries used an open-weight model from Cohere Labs and targeted a small group of readers who opted in.
The trial sparked strong pushback from Wikipedia’s volunteer editors. Many feared the summaries could undermine the platform’s reputation for reliability. One editor warned it would cause “immediate and irreversible harm” to readers’ trust. Others criticized the lack of editorial control over the AI-generated content, fearing it would erode years of policy work.
The Wikimedia Foundation paused the trial after two days but affirmed ongoing interest in accessible content features. Human editors will continue to play a central role in deciding what appears on Wikipedia.
Bloomberg recently corrected dozens of AI summaries on its articles for accuracy, and other platforms face similar issues. These examples demonstrate that, despite AI’s promise to streamline information, maintaining trust and factual accuracy remains a priority.
TF Summary: What’s Next
Meta’s AI summaries on WhatsApp and Instagram intend to enhance the user experience, but their rollout requires cautious consideration to ensure privacy and reliability. Wikipedia’s delayed rollout shows the importance of editorial oversight with AI-driven content.
Both cases present challenges related to automation and accuracy. The future of AI summarization hinges on enhancing trustworthiness while increasing information accessibility.
To ensure the responsible development and deployment of AI moderation, users, developers, and platforms must collaborate effectively. Open and direct collaboration is crucial to establish AI systems that prioritize privacy, maintain credibility, and facilitate informed reading experiences for users.
— Text-to-Speech (TTS) provided by gspeech


