A new AI world model trains self-driving cars to imagine the road before they drive it.
Self-driving cars learn from data. Now they also learn from imagination. Waymo reveals a new AI system built with help from Google DeepMind. The tool is called the Waymo World Model. It uses DeepMind’s Genie 3 technology to simulate driving scenarios with stunning realism.
Instead of waiting for rare events to happen on real streets, Waymo generates them in software. The model produces synchronized 2D video and 3D lidar outputs. It lets engineers change routes, weather, lighting, and road conditions with prompts.
In short, Waymo’s cars can rehearse before they drive. That shift changes the future of autonomous mobility.
What’s Happening & Why This Matters
A world model replaces passive training

Autonomous vehicles once relied heavily on recorded footage. Cars drove real routes. Engineers collected data. Algorithms learned from past mistakes. The model flips that logic.
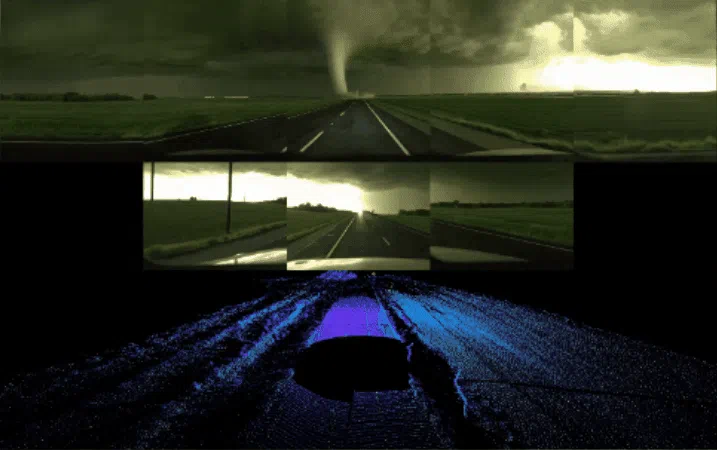
Waymo feeds dashcam video into the world model. The system then generates matching lidar sensor data. It reconstructs how the car would have perceived that scene in full 3D.
Cameras capture detail. Lidar captures depth. Together they simulate reality.
Waymo and DeepMind do not simply plug Genie 3 into a dashboard. They apply specialized post-training methods so the system produces consistent 2D and 3D outputs of the same scenario.
That alignment matters. A self-driving system must understand distance, speed, and spatial relationships. Video alone lacks enough depth precision. Lidar supplies that missing geometry.
The result feels closer to a physics engine than a video generator.
Driving action control changes the game
Waymo introduces what it calls driving action control. Engineers can take recorded footage and prompt the model to alter the car’s route. What happens if the vehicle turns left instead of right? Or a pedestrian crosses earlier? What if traffic density increases?
The world model shows the outcome. It simulates the alternate path, even generating consistent LiDAR maps. It predicts how the AI would react. This approach moves beyond reconstruction. Older simulations rebuilt past events. The new model explores hypothetical ones.
That capability accelerates training cycles. Instead of waiting for rare edge cases, Waymo can create them.
Synthetic Mutation vs. Synthetic Fabrication
The Waymo World Model can build fully synthetic scenes. Yet the company appears more focused on mutation. Engineers alter conditions within real video. They change the time of day, introduce rain or fog, or apply new signage. They reposition vehicles.
The models even drop an elephant in the road. The point is stress testing.
Waymo began operations in sunny cities such as Phoenix. Harsh weather remained limited. As expansion moves into Boston and Washington, D.C., weather variability increases.
The world model prepares cars for snow, rain, glare, and urban density. It does not wait for a blizzard, but rather simulates one.
Setting Waymo Apart
Competitors often rely heavily on camera-only systems. Waymo continues betting on multimodal sensing. The world model reinforces that philosophy. It generates lidar alongside video. It trains the AI using both sensory streams.
That design improves spatial reasoning. A camera can misjudge distance in glare. Lidar reads shape and depth. In autonomous driving, millimeters matter.
Waymo’s integrated approach reflects long-term thinking. The system learns how surfaces reflect. It learns how obstacles move. It learns how shadows distort perception. Simulation sharpens those instincts.

Genie 3 as a Foundation
DeepMind’s Genie 3 powers the backbone. Earlier demonstrations of Genie 3 ranged from impressive realism to uncanny visuals. Yet Waymo believes the model achieves sufficient fidelity to improve autonomous behavior.
The success depends on realism. If simulations drift too far from reality, training degrades. If they closely match physics and perception, performance improves.
Waymo argues the technology has matured. The model produces consistent depth, motion, and sensor alignment. That consistency builds trust inside the system.
Scaling: Better Training, Lower Risk
Self-driving fleets accumulate millions of miles of data. Yet rare scenarios remain rare. A pedestrian is darting across an icy intersection. A truck is swerving under low visibility. Debris is flying into a lane.
Collecting the events in the wild risks damage. Simulating them carries no risk. The Waymo world model AI driving system compresses time.
Instead of waiting years to encounter enough edge cases, engineers can generate thousands within days. That compression drives faster iteration. Faster iteration drives safer deployment.

The Market vs. Reality
Waymo expands into cities with complex road geometry and dynamic weather. Boston features narrow streets. Washington, D.C., features heavy pedestrian flows and roundabouts. The world model prepares the AI for these environments before rollout.
Preparation reduces trial-and-error on public streets. Public trust hinges on safety metrics. Simulation improves confidence before exposure.
A Philosophical Shift
Autonomous driving once focused on reactive learning. Autonomous driving enters predictive rehearsal. The AI imagines outcomes before acting.
This mirrors human learning. Pilots train in simulators. Surgeons practice on digital models. Athletes visualize plays. Self-driving cars do the same.
The Waymo world model AI driving framework moves autonomy closer to cognitive rehearsal. That step feels subtle. It is not.
The Competitive Response
Waymo leads U.S. robotaxi deployments. Yet competition intensifies. Other players experiment with camera-only stacks. Some explore generative AI. Few combine large-scale multimodal sensing with world models at this depth.
DeepMind’s involvement strengthens Waymo’s technical moat. World models also extend beyond driving. They represent a general AI capability: simulating reality, testing decisions, and refining behavior. Autonomous mobility is a proving ground
Risks and Limitations
Simulation quality is critical. If Genie 3 produces unrealistic physics, the system could learn flawed behavior. Edge cases must reflect real-world dynamics.
Waymo continues validating outputs against actual fleet data. The company does not abandon physical testing. It augments it.
The hybrid strategy balances innovation with caution.
TF Summary: What’s Next
Waymo integrates DeepMind’s Genie 3 into a powerful world model that generates synchronized video and lidar simulations. Engineers mutate real footage, test alternate routes, and simulate extreme conditions without risking real vehicles.
MY FORECAST: Waymo’s World Model AI-driven driving becomes standard across the industry. Simulation-first training reshapes autonomous development. Cities adopt stricter safety metrics. Companies that master multimodal world modeling lead the next phase of autonomy.
— Text-to-Speech (TTS) provided by gspeech | TechFyle